|
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY执行摘要
Objective目的
本咨询方案的目的是提供项目管理咨询的公司,larels项目的律师事务所,在组织结构(方便,1999)。
larels LLP的项目概述
larels项目律师事务所进行建设和物业顾问在英国的业务活动作为一个项目组织(Hobday,2000)。其总部位于伦敦,其分支机构位于哈洛和工作以及。公司成立于1985 larels项目提供造价咨询和建筑服务的公共和私营部门的客户,正在新建和翻新工程,由一个姐姐和一个哥哥。larels项目已发展到120个员工unitise大小随后。在2014-2015年营业额大约是£1120,larels项目律师事务所的经营环境是由四部分组成,包括文化、社会结构、物理结构、技术。对larels项目律师事务所的企业文化是体现在在一个值得注意的计划开始在工程项目群管理的战略方法早期参与是成功战略的基本信念。larels项目律师事务所承诺提供非凡的伙伴关系,始终将领导服务。larels项目律师事务所旨在创造建筑,超过客户的标准和期望通过努力工作,通过重视客户的重要性。larels项目律师事务所旨在基于事实的总部位于伦敦的构建不同的企业内部社会环境,为英国的社会商业环境。项目的larels LLP的物理环境是现代的,艺术的和鼓舞人心的工人。项目的larels LLP技术环境不断在建和正在装修扩大员工的知识和提高项目管理的效率。larels项目律师事务所组织的工作提供一个详尽的服务来自不同领域的专业知识,如项目管理、成本管理、健康与安全、建筑测量、发展监测/商业尽职调查,和能源与可持续发展。larels项目律师事务所工作的各个环节如教育、艺术、休闲、居住、商业和零售。
The objective of this consulting proposal is to advise the project management consultancy firm, Larels Projects LLP, on an organisational structure (Handy, 1999). An outline proposal for an optimum structure based on the outline of the company’s business activity and staff base will be recommended.
Overview of Larels Projects LLP
Larels Projects LLP conducts Construction and Property Consultancy business activities in UK as a project-based organisation (Hobday, 2000). Its head office is located in London, with its branches located in Harlow and Woking as well. Larels Projects LLP is established in 1985 to provide cost consultancy and building surveying services to the public and the private sector clients that are undertaking new building and refurbishment projects, by a sister and a brother. Larels Projects has developed to unitise a staff size of 120 subsequently. Its turnover in 2014—2015 was around £11.2m. The business environment of Larels Projects LLP is composed of four parts, including culture, social structure, physical structure, and technology. The organisational culture of Larels Projects LLP is reflected in its belief in that early engagement in strategic approaches of the Project Management group at the beginning of a noteworthy programme is essential to a successful strategy. Larels Projects LLP promised to offer an extraordinary partnership led service that is consistently incorporated. Larels Projects LLP aims at creating buildings that exceed clients’ standards and expectations through hard working and through valuing the importance of customers. Larels Projects LLP aims at constructing a diverse internal social business environment based on the fact that the head office lies in London, as an external social business environment in UK. The physical environment of Larels Projects LLP is modern, artistic and inspiring for workers. The technology environment of Larels Projects LLP is constantly under construction and being renovated to expand the knowledge of worker and to improve the efficiency in projects management. Larels Projects LLP organises work to deliver an exhaustive service from various areas expertise such as Project Management, Cost Management, Health and Safety, Building Surveying, Development Monitoring / Commercial Due Diligence, and Energy and Sustainability. Larels Projects LLP works in various sectors such as Education, Arts and Leisure, Residential, and Commercial and Retail.
Proposal of organisational structure
Consultancy firms often uses static organisation design models, such as the star model (Galbraith, 1995) and the 7—S model (Waterman et al, 1980), to recognise a scope of elements which can influence the organisational design (Jones, 2013). There are six fundamental elements of an organisational structure, namely specialisation, chain of command, span of control, centralisation or decentralisation, formalisation, and departmentalisation.
Classical types of organisational structure have emerged and developed in 1947 (Weber, 1947). The five classical grouping models are Functional Organisations that are common in single-project organisations, Geographical Organisations that are common in multi-location organisations, Organisations by Product that are common in organisations with multiple projects and foundations, Organisations by Customer / Market that are common in smaller organisations focusing on customers narrowly or larger non-profit organisations where the customers are in alignment with their programs, and Matrix Structure that are common in global or nationwide organisations that are large and sophisticated. Given the fact that Larels Projects LLP spans three locations, such as London, Harlow and Woking. The organisational structure of Larels Projects LLP shall first be on a geographical model. At the same time, since Larels Projects LLP offers different types of services such as Project Management, Cost Management, Health and Safety, Building Surveying, Development Monitoring / Commercial Due Diligence, and Energy and Sustainability, the organisational structure of Larels Projects LLP can be the Project Organisation Structure (Divisional Structure) built on a base Geographic Structure, that is a Geographic Divisional Structure. Based on the fact that Larels Projects LLP currently has 120 staff members, a Functional Structure will be too simple for Larels Projects LLP as it functions in three locations and provides different services, and a Matrix Structure will be too complicated for Larels Projects LLP as the Matrix Structure is for large and global organisations that provide a wide variety of products and services.
Geographic Structure经济地理格局
Firstly, the organisational structure of Larels Projects LLP is based on a Geographic Structure Design (Worren,2012) in three regions: London, Harlow and Woking as shown in Figure 1. It is important to use the Geographic Structure (Pugh, 2007) as a base structure because the outcomes of the same project can be very different from city to city. For example, Larels Projects LLP delivers Cost Management services to building companies. The Cost Management will be much more expensive in London than in Harlow or Woking. Therefore, it is important to differentiate the organisation among geographic factors first.
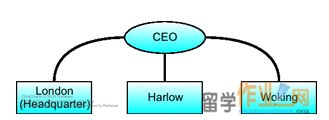
Figure 1: Geographic structure of the organisation structure of Larels Projects LLP.
Geographic speaking, the Woking office is only 22 mins of train away from the London Headquarter office but Harlow is two hours of train away from London. Therefore, the Harlow office and London office can share some staff members if needed. The most important decision making managers shall be based in the London Headquarter to better communicate in big decisions. If Harlow needs technical support, the London Headquarter will be able to respond very quickly. Therefore, the Woking office needs relatively more independent set of staff members from the London office such as IT Services staff members.
Geographic Structure into Geographic Functional Structure
Secondly, each of the three branches of Larels Projects LLP from the base geographic structure will need different functionals to operate independently because for example it will be inconvenient for London office and Harlow office to share one Information Technology (IT) department. Therefore, the Geographic Functional Structure will allow each brach to have its own Human Resource (HR) Department, Accounting Department, IT Department, Communication & Marketing Department, and Project Department. This Geographic Functional Design is shown in Figure 2.
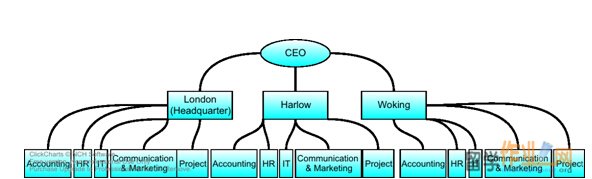
Figure 2: Geographic Functional Design of organisational structure for Larels Projects LLP.
Among the 120 staff members at Larels Projects LLP, the human resource in Accounting, HR, IT and Communication & Marketing will be arranged as the follows. The two Accountants and the four Accountants Assistants will be distributed evenly in numbers into the three offices, where the London Headquarter will have one Accountant and one Assistant because the office is larger. One HR director and one HR assistant will be placed in the HR department in the London office. The rest one HR Manager and one HR assistant will be placed in the Harlow and Woking offices. The IT Service Manager will be placed in the IT office in London Headquarter. The other two IT Services Assistants will be placed in the IT offices in Harlow and Woking.
Geographic Functional Structure into Geographic Functional Project Organisation Structure#p#分页标题#e#
The value creation is the direct product and output from the Project Department from the London office, Harlow office and Woking office. Therefore, it is meaningful to design the organisational structure of the Project Department in more details. Because each Project Department from the London office, Harlow office and Woking office in the Larels Projects LLP will provide a variety of services such as Project Management (PM), Cost Management (CM), Health and Safety (H&S), Building Surveying (BS), Development Monitoring / Commercial Due Diligence (DM / CDD), and Energy and Sustainability (E&S), the Project Organisation Structure is built on each Project Department in each branch to form a Geographic Functional Project Organisation Structure. That is to say, for each Project Department in all the three offices, project based differentiation will be made to provide a variety of services. The Project Organisational Structure for each of the Project Department in Figure 2 is shown in Figure 3. Among the 120 staff members at Larels Projects LLP, the six Senior Building Surveyors, eight Building Surveyors and one Partner in Monitoring Surveying will be distributed into the BS department under the Project Department. The one Partner in Cost Management, six Senior Quantity Surveyors and eight Quantity Surveyors will be distributed into the CM department under the Project Department. The three energy & Sustainability Consultants will be distributed under the E&S department under the Project Department (one staff member per office). The three CDM consultants, the two Partners in Project Management, the two newly appointed Graduate Project Managers and the four Graduate Project Managers with some client-facing responsibilities will work for the PM department under the Project Department (one staff member per office). The newly appointed Graduate Project Managers can work under the guidance of existing CDM consultants and the two Partners in Project Management. The one Senior Monitoring Surveyor and four Monitoring Surveyors will work for the DM / CDD department under the Project Department.
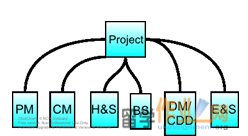
Figure 3: Project Organisation Structureof Project Department in London, Harlow and Woking offices.
The Geographic Functional Project Organisation Structure Design of Larels Projects LLP shown in Figures 2 and 3 has six elements: specialisation, chain of command, span of control, centralisation or decentralisation, formalisation, and departmentalisation.
Centralisation V.s. Decentralisation
In this organisational structure, the decentralisation structure will be applied because there are several management layers in this structure. It will be much faster and more efficient for the Project Managers to make technical decisions from the surveys conducted by the Senior Building Surveyors and Senior Quantity Surveyors than for a CEO to do so. What kind of decisions will be made by each layer of management will be explained as the following.
On the top level, the CEO and the two Non-executive Directors in this designed organisational structure will focus on long term decisions such as the vision of Larels Project LLP, provision of appropriate resources, constructing the business organisation culture and overseeing the company’s performance. The CEO and the two Non-executive Directors will work out the strategic direction for developing Larels Project LLP such as whether a new office shall be built and whether a new line of service shall be provided from the market’s demand. The CEO and the two Non-executive Directors shall also work out a balance of human resources and technology resources among the three offices in London, Harlow and Woking to optimise the use of resources to create the most values. The CEO and the two Non-executive Directors shall also sculpt and characterise the culture in the organisation such as what attitudes and behaviours are encouraged, and the cultures shall be consistent at all management levels. The CEO and the two Non-executive Directors will also oversee the value creation as the performance of the company and compare the performance of the company to the goal.
On the second level of management under the CEO level lie the Finance Director, the HR Director and all the other managers. The Finance Director is responsible for analysing the balance sheet of the company, prepare the strategic plan and forecast quarterly the insight to the CEO and Non-executive Directors. The HR director will be help estimate the HR, consider various options to address the business challenges and help develop the culture in the organisation. Other managers will work in their specific areas. For example, the Communications & Marketing Manger will organise market research and work out marketing strategies. The Facilities Manager will maintain the smooth functioning of the physical environment such as the printers and the lights. The IT Services Manager will seek new technologies for the organisation’s safety and efficiency in functioning. For example, the IT Services Manager may want to consider using virtual machine to store the company’s data for better security. The Project Directors will lead the Project Managers and the Senior Project Managers by overlooking the quality and performance of all the services delivered by the surveyors and the consultants. The Project Managers and Senior Project Managers will be in direct contact with the Surveyors and Consultants, to ensure that the quality of the service delivered meets the company’s standard. The Project Managers and Senior Project Managers are expected to know some details of all the service that are provided such as Project Management (PM), Cost Management (CM), Health and Safety (H&S), Building Surveying (BS), Development Monitoring / Commercial Due Diligence (DM / CDD), and Energy and Sustainability (E&S). They are expected to hold weekly meetings to listen to the reports from the Surveyors and Consultants. Managers at this level can make their decisions independently as long as they are not against the organisation vision and culture.
On the next level of management lies the assistants, the surveyors and the consultants that are the closest to the details of subject matters. The Communications & Marketing Assistant will implement the market research plan and marketing strategy made by the Communications & Marketing Manger. The Surveyors and Consultants are very important parts of the organisation structure as they are in direct responsibility in value creation of the organisation to the external environment and their performance and quality of services will directly impact the reputation of Larels Projects LLP. The Surveyors and Consults are expected to know a great deal of details of the services they are providing. The Surveyors and Consultants are expected to make independent decisions on the technical level. For example, the Monitoring Surveyors are allowed to draw their own independent conclusions on emerging problems and to bring them to the attention of the authorities.
As long as the CEO will review the decisions made by the Directors and the Directors will review the decisions made by the Managers, the decentralised organisational structure will work more efficiently than a centralised structure. As the area of services provided by the company requires both the technical expertise from the Surveyors and Consultants and the vision set by the CEO.
Rationalisation of the proposed organisational structure提议的组织结构合理化
The top level of the organisational structure is chosen to be the Geographic Organisation Structure because of the geographic characteristics of different offices. As the building construction consulting projects will heavily depend on the local characteristics of the area, such as the Cost Management in London will be much more expensive than Harlow and Woking, it is reasonable to differentiate the geographic characteristics between the London, Harlow and Woking offices first. As the Finance Directors and HR Directors will overlook the business performance and value creation in the three offices, the next level is to differentiate the staff members in each offices by different department through building a Functional Structure on top of Geographic Functional Structure. The main business activity that accounts for value creation is done by the technical staff members such as the Surveyors and the Consultants. It is better to put the Surveyors and the Consultants at the bottom level of management so that they can focus on the technical issues in the services and their work can be better directed and reviewed by the Project Directors and Project Managers. This Geographic Functional Project Organisational Structure Design considers the external business environment by considering the geographic features of the three different offices. This design also consider the internal business environment by allowing a decentralised organisational design to better differentiate the management work from the CEO as an example and technical work done by the Surveyors and the Consultants as an example.
The value of Larels Projects LLP are directly created by the services delivered by the Surveyors and Consultants. It is under the supervision of Project Directors to deal with any issues and to set the priority between projects. The value creation is made more efficient with the technical support from the IT department and a better distribution of human resources under the advise from the HR Director (Daintyet al, 2013) because of the impact of HR on the organisational performance (Beckeret al, 1996). The physical environment of value creation is guaranteed by the Facilities Manager. The value creation is reviewed by the Finance Director. The CEO will act in between the internal organisation performance and the external shareholders. The CEO will set up a general healthy business environment for better value creation.#p#分页标题#e#
The diversity of the organisational design
This organisational structure will value diversity and inclusion. An organisation structure with diverse backgrounds of staff members will bring interesting ideas and creations into the organisation. Diversity is not only about employment of staff members coming from different countries and different cultures. Diversity is also about accepting the difference between different cultures and different countries. Staff members in this organisational structure design will be employed not only by their ability but also by considering their diverse background. Staff members within this organisation will join various social events to mingle and to get to know each other. Staff members of this organisation will travel between the three offices to think outside their boxes and to hear the issues that rise in other offices. Staff members in this organisation will also be given chances to travel abroad for conferences and seminars, not just for technical aims but also for cultural exchange. The HR Assistants will be responsible to take several cultural course to bring cultural diversity into awareness among all the staff members.
Summary
In this proposal, a Geographic Functional Project Organisational Structure is designed with a decentralisation decision making structure that allows the CEO to focus on long term vision and the bottom Surveyors and Consultants to focus on technical insights. This design considers maximising the value creation from the Surveyors and Consultants under the vision of the CEO and the guidance of other managers. This design also allows each office to hire new staff members if needed. This organisation is also designed to have a diverse culture.
Reference文献
Becker, B.,Gerhart, B. (1996). The impact of human resource management on organizational performance: Progress and prospects. Academy of management journal, 39(4), pp. 779–801.
Dainty, A., Loosemore, M. (Eds.). (2013). Human Resource Management in Construction: Critical Perspectives. Routledge.
Galbraith, J. (1995).Designing Organisations: An executive briefing based on strategy, structure and process. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Handy, C. (1999).Understanding Organisations, 4th Edition, Penguin, London.
Hobday, M. (2000). The project-based organisation: an ideal form for managing complex products and systems? Research policy, 29(7), pp. 871–893.
Jones, G. R. (2013). Organizational theory, design, and change, 7th Ed. Harlow: Pearson.
Pugh, D. S. (2007). Organization theory: selected classic readings. Penguin UK.
Waterman, R., Peters, T. and Phillips, J. R. (1980). Structure is not organisation. Business Horizons, 23 (3),pp. 14–26.
Weber, M. (1947).The Theory of Social and Economic Organisation. New York: Free Press.
Worren, N. (2012).Organisation Design. Pearson, Harlow.
|
 |
|||
| 网站地图 |

